CALL TODAY 646-846-1136 | EMAIL
Surgical Experts Dedicated to Improving Lives
At Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery PLLC, Dr. Valery Dronsky and his staff of medical professionals provide compassionate care with the highest ethical & professional standards. In our state of the art facility, we offer surgical services using only the most cutting edge and current procedures and treatments. We specialize in general surgery, including extensive experience in performing hernia repair surgery. Our expertise is in minimally invasive surgery and robotic surgery. Minimally invasive and robotic surgery often allow patients to experience easier recovery than traditional open surgery. They also allow for more precise and less traumatic surgery. When robotic and minimally invasive surgery is not an option, we are also skilled and experienced in traditional open surgical procedures.
Dr. Dronsky is an experienced and highly skilled surgeon having undergone extensive training in school, residency and fellowships. He practices medicine with ethical behavior, compassion and superb bedside manner. In the operating room he exhibits precision mechanical abilities, analytical thinking and the ability to visualize tissue in three dimensions. These innate and learned skills allow Dr. Dronsky to be one of the most dexterous and skilled professionals in New York City and the Country.
Call us: 646-846-1136
PATIENT TESTIMONIALS
Recent Awards
We are honored and deeply appreciative to have consistently received prestigious awards and recognition year after year, establishing us as one of New York’s foremost hospitals for a wide range of general surgeries, safety measures, specialized procedures, and overall excellence in healthcare. At Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery, our unwavering commitment lies in delivering exceptional care and unwavering support to our patients, guaranteeing their safety and successful recovery throughout their entire surgical experience.
Hospital Quality Awards
 America’s 50 Best Hospitals Award™ (2023, 2022)
America’s 50 Best Hospitals Award™ (2023, 2022)
Top 1% in the nation for providing the highest clinical quality year over year.

America’s 100 Best Hospitals Award™ (2021)
Top 2% in the nation for consistently delivering clinical quality year over year.

America’s 250 Best Hospitals Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021)
Top 5% in the nation for consistently delivering clinical quality.

Patient Safety Excellence Award™ (2023, 2022)
Top in the nation for providing excellence in patient safety by preventing infections, medical errors, and other preventable complications.
Specialty Clinical Quality Awards

America’s 100 Best Hospitals for Cardiac Care Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019)
Superior clinical outcomes in heart bypass surgery, coronary interventional procedures, heart attack treatment, heart failure treatment, and heart valve surgery.

America’s 100 Best Hospitals for Coronary Intervention Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019)
Superior clinical outcomes in coronary intervention procedures (angioplasty with stent).

America’s 100 Best Hospitals for Prostate Surgery Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021)
Superior clinical outcomes in prostate removal surgery and transurethral resection of the prostate.
Click to see all of our Healthgrades best doctors awards



Visit our main website at www.LenoxHillMinimallyInvasiveSurgery.com
Blog Posts are Below:
Hernia Repair Surgery – NYC Surgeon
Hernia Repair Surgery: Steps, Benefits, Side-Effects, Precautions & Prognosis
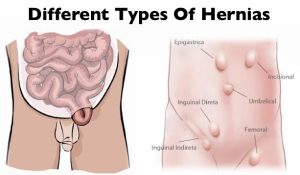 Hernia repair surgery entails the application of instrumental and manual procedures for correcting herniation of tissues or viscera including groin, abdomen, brain, and diaphragm. Internal organs, composed of tissues, could get herniated or bulged, forcing them to protrude via the wall encasing them. Hernias involving the groin (an inguinal hernia) and the umbilical cord (an umbilical hernia) are two of the most prevalent forms of a hernia.
Hernia repair surgery entails the application of instrumental and manual procedures for correcting herniation of tissues or viscera including groin, abdomen, brain, and diaphragm. Internal organs, composed of tissues, could get herniated or bulged, forcing them to protrude via the wall encasing them. Hernias involving the groin (an inguinal hernia) and the umbilical cord (an umbilical hernia) are two of the most prevalent forms of a hernia.
Since a hernia does not heal on its own but rather expands over time, it is crucial that you opt for surgical treatment to avoid unnecessary/preventable complications in the long run. Hernia surgery, usually performed on an outpatient basis, is a moderately simple operation that can help remedy the organ’s bulging and restore it to its original position.
Steps
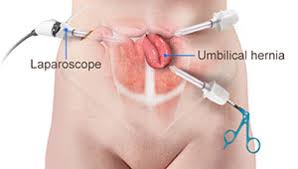 Two of the most popular types of hernia repair surgery is ‘herniorrhaphy’ and ‘hernioplasty’. Herniorrhaphy-the traditional hernia repair technique-is still conducted extensively where the surgeon makes a wide and long notch over the herniated organ. Thereafter, the physician removes the protrusion and reinstates the dislodged organ or tissues to its actual site.
Two of the most popular types of hernia repair surgery is ‘herniorrhaphy’ and ‘hernioplasty’. Herniorrhaphy-the traditional hernia repair technique-is still conducted extensively where the surgeon makes a wide and long notch over the herniated organ. Thereafter, the physician removes the protrusion and reinstates the dislodged organ or tissues to its actual site.
Finally, the doctor sutures the hole in the muscle via which the protuberance developed, sterilizes the incision, and sews it up. Hernioplasty is very much similar to herniorrhaphy procedurally excepting that in the final step, the surgeon overlays a sterile mesh (produced from animal tissues or polypropylene) on the muscular notch rather than suturing it. The nature or type of your herniation will determine the mode of repair surgery you’ll need to opt for.
Strangulated, reducible, and irreducible hernias are the three most widespread kinds of hernias. Both of the aforementioned surgical operation procedures can be carried out using a laparoscope or via open surgery.
Benefits
Both hernioplasty and herniorrhaphy are straightforward and uncomplicated surgical repair processes that take about 30-40 minutes to complete. You won’t feel any pain as the surgery will be done using either local or general anesthesia. Majority of patients are discharged from the hospital or medical center on the very day the laparoscopic surgery is performed. The usual benefits of the laparoscopic repair operation include:-
- Very short duration of stay
- Faster healing
- Reduced pain post surgery
- Quicker return to normal life
- Minimal costs (including all the expense heads)
- Lower risks of infection
Side Effects
The side effects of this type of surgery, most of which are rare, involve:-
- Swelling and redness around the incision or opening
- Blood clot
- Mesh pain
- Urinary tract infection
- Urinary incontinence
- Infection
- Difficulty urinating
- Hernia recurrence
- Neuralgia or nerve damage
- Constipation
- Kidney failure or complications
- Breathing problems or pneumonia
Precautions
You must abide by the surgeon’s instructions once you return home (which are usually on the same day the surgery is carried out) for a speedy recovery. Take all the prescribed medications on time, including the anti-inflammatory drugs for minimizing the possibilities of incision swelling. Contact your surgeon instantly if you’ve recurrent spells of fever, coughs, chills, nausea, abdominal swelling, bleeding as well as experience difficulty in urinating. Make sure you get sufficient rest for at least two weeks following the operation so that you can get back to work at the earliest.
Prognosis
Most hernia surgeries are effective, enabling patients to recover fully within 4-6 weeks. A typical person who has undergone hernia repair surgery can resume normal activities 2 weeks after the procedure.
Concluding Remarks
Opting for a surgical procedure for remedying a hernia is highly recommended not only for avoiding complications which could take a fatal turn (though very rare) but also for going back to leading a normal life. You can make an appointment with our general surgeon for a detailed, one-to-one consultation.
References
- http://www.medtronic.com/us-en/patients/treatments-therapies/hernia-surgery/about-recovery.html
- https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/inguinal-hernia#1
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319753.php
- https://www.highgatehospital.co.uk/things-you-need-to-know-hernia-operation/
- https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/need-surgery-hernia#1
- http://columbiasurgery.org/news/2014/04/15/hernias-what-you-need-know
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hernia_repair
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/6905-laparoscopic-surgery-for-hernia-repair/risks–benefits
General Surgery
Here are some brief descriptions about the different types of general surgery we perform:
Laparoscopic surgery
This is a relatively new specialty dealing with minimal access techniques using cameras and small instruments inserted through 0.3 to 1 cm incisions. Robotic surgery is now evolving from this concept (see below). Gallbladders, appendices, and colons can all be removed with this technique. Hernias are now repaired mostly laparoscopically. Most bariatric surgery is performed laparoscopically.[citation needed] General surgeons that are trained today are expected to be proficient in laparoscopic procedures.
Colorectal surgery
General surgeons treat a wide variety of major and minor colon and rectal diseases including inflammatory bowel diseases (such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease), diverticulitis, colon and rectal cancer, gastrointestinal bleeding and hemorrhoids.
Endocrine surgery
General surgeons are trained to remove all or part of the thyroid and parathyroid glands in the neck and the adrenal glands just above each kidney in the abdomen. In many communities, they are the only surgeon trained to do this. In communities that have a number of subspecialists, other subspecialty surgeons may assume responsibility for these procedures.
Surgical oncology
Surgical oncologist refers to a general surgical oncologist (a specialty of a general surgeon), but thoracic surgical oncologists, gynecologist and so forth can all be considered surgeons who specialize in treating cancer patients. The importance of training surgeons who sub-specialize in cancer surgery lies in evidence, supported by a number of clinical trials, that outcomes in surgical cancer care are positively associated to surgeon volume—i.e., the more cancer cases a surgeon treats, the more proficient he or she becomes, and his or her patients experience improved survival rates as a result. This is another controversial point, but it is generally accepted—even as common sense—that a surgeon who performs a given operation more often, will achieve superior results when compared with a surgeon who rarely performs the same procedure. This is particularly true of complex cancer resections such as pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic cancer, and gastrectomy with extended (D2) lymphadenectomy for gastric cancer. Surgical oncology is generally a 2 year fellowship following completion of a general surgery residency (5-7 years).
Contact us at 646-846-1136 to schedule an appointment.
Soft Tissue & Skin Surgery: Procedures for Lesions, Tumors, and Infections
 This guide explores common soft tissue and skin conditions that may necessitate surgery, the types of surgical procedures used, and what patients can expect from the recovery process.
This guide explores common soft tissue and skin conditions that may necessitate surgery, the types of surgical procedures used, and what patients can expect from the recovery process.
The skin, the body’s largest organ, and soft tissues play a critical role in protecting us from infections, regulating body temperature, and enabling the sense of touch. However, various conditions, including lesions, tumors, and infections, can affect the skin and underlying soft tissues, causing discomfort, cosmetic concerns, and even potential health risks. When conservative treatments are insufficient, surgical intervention may be required to address these issues effectively.
Common Conditions Requiring Soft Tissue & Skin Surgery
Many skin and soft tissue conditions may require surgical intervention, especially when they pose a health risk or affect quality of life. Here are some of the most common conditions treated with surgery:
1. Skin Lesions
Skin lesions include a broad range of growths or abnormal patches on the skin, such as moles, warts, and cysts. While many lesions are benign, some may need to be removed due to cosmetic concerns, discomfort, or suspicion of malignancy. In particular, suspicious moles or lesions may be removed for biopsy to rule out skin cancer.
2. Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer and can manifest as basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or melanoma. Surgical removal is often the primary treatment for skin cancer, especially when it is detected early. Removing cancerous tissue can prevent the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
3. Lipomas
Lipomas are benign, soft, fatty growths that develop under the skin. They are generally painless but can grow large and become bothersome or cosmetically unappealing. Surgical removal of lipomas is often recommended if they cause discomfort or interfere with movement.
4. Soft Tissue Sarcomas
Soft tissue sarcomas are rare but potentially aggressive malignant tumors that can develop in the soft tissues, including muscles, fat, and connective tissue. Surgery is usually the first line of treatment for soft tissue sarcomas to remove the tumor and prevent it from spreading.
5. Infections and Abscesses
Infections in the skin and soft tissues can lead to abscesses, which are pockets of pus that form as the body fights off infection. Abscesses can cause significant pain, swelling, and fever. Surgical drainage or removal is often necessary to eliminate the infection and promote healing.
Types of Soft Tissue & Skin Surgery
There are several surgical options available for treating skin and soft tissue conditions, each tailored to the specific type of condition. Here are some of the most common procedures:
- Excisional Biopsy: This procedure involves removing the entire lesion or growth along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete removal. It is commonly used for suspicious moles, skin cancer, and other lesions requiring a definitive diagnosis.
- Mohs Surgery: Mohs surgery is a specialized procedure primarily used to treat skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. The surgeon removes thin layers of skin one at a time, examining each under a microscope to ensure complete removal of cancerous cells while sparing as much healthy tissue as possible.
- Wide Local Excision: In cases of melanoma or other aggressive skin cancers, a wide local excision is performed to remove the cancer along with a larger margin of healthy tissue to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Incision and Drainage: This procedure is used to treat abscesses by making a small incision to drain the pus and relieve pressure. It promotes healing by reducing the infection and is often followed by antibiotic therapy.
- Lipoma Removal: Lipomas are usually removed through a minor surgical procedure. The surgeon makes a small incision and carefully removes the fatty growth. Lipoma removal is often performed under local anesthesia and has a short recovery period.
- Soft Tissue Sarcoma Resection: For soft tissue sarcomas, surgery aims to remove the entire tumor along with a surrounding margin of healthy tissue. This procedure may be performed in combination with radiation therapy or chemotherapy to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Minimally Invasive Techniques for Soft Tissue & Skin Surgery
For certain skin and soft tissue surgeries, minimally invasive techniques can be used to reduce recovery time and minimize scarring. These techniques include:
- Laser Surgery: Laser surgery is used for specific types of lesions, including warts, certain types of birthmarks, and small skin cancers. Laser treatment is precise and reduces damage to surrounding tissue.
- Endoscopic Surgery: For some soft tissue tumors, an endoscopic approach can be used. This involves using a small camera and specialized instruments inserted through tiny incisions to remove the tumor. This approach is particularly beneficial for deeper or larger tumors.
- Minimally Invasive Lipoma Removal: Lipomas located in hard-to-reach areas or those that are large may be removed with minimally invasive techniques, using smaller incisions to reduce scarring and recovery time.
Benefits of Soft Tissue & Skin Surgery
Surgical intervention for skin and soft tissue conditions offers several benefits, including:
- Relief from Symptoms: For painful or bothersome lesions, tumors, or infections, surgery can provide immediate relief from symptoms and improve comfort.
- Improved Aesthetics: Removal of visible lesions or growths can improve appearance, especially for lesions located in prominent areas like the face or neck.
- Reduced Risk of Infection Spread: In cases of abscesses and infections, surgical drainage prevents the spread of infection to surrounding tissue and speeds up recovery.
- Enhanced Diagnosis and Treatment: Removing suspicious lesions or tumors allows for a definitive diagnosis and, in cases of cancer, a chance to prevent further spread.
- Prevention of Complications: Early removal of tumors, lesions, or infected areas reduces the risk of complications and improves overall health outcomes.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Recovery after soft tissue and skin surgery varies based on the type of procedure and the location of the surgical site. Here’s what most patients can expect during recovery:
- Pain Management: Mild pain and discomfort are common after surgery, especially for larger excisions. Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications may be recommended.
- Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and ensure healing. Patients may need to keep the surgical area clean, apply prescribed ointments, and follow any specific instructions from their surgeon.
- Activity Restrictions: Depending on the size and location of the incision, patients may need to avoid strenuous activities until the wound is fully healed. Light activities like walking are usually encouraged.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary, especially for patients who had cancerous lesions removed, to monitor healing and check for any recurrence.
- Scarring and Cosmetic Considerations: Minimally invasive techniques help reduce scarring. However, patients should follow their surgeon’s advice on minimizing scar tissue, which may include applying scar-reducing creams or protecting the area from sunlight.
Improving Quality of Life through Soft Tissue & Skin Surgery
Soft tissue and skin surgeries offer a range of benefits, from relieving discomfort and improving appearance to providing definitive treatments for serious conditions like skin cancer. Patients often report enhanced quality of life following successful surgery, as they experience less pain, improved mobility, and greater confidence. Early intervention, especially for suspicious or bothersome lesions, can also lead to better health outcomes by preventing the progression of potentially serious conditions.
If you’re experiencing discomfort, pain, or concerns about any skin or soft tissue lesions, tumors, or infections, consulting with a skilled general surgeon can help you explore treatment options. Surgical intervention may offer relief, and with the latest techniques, many procedures have shorter recovery times and minimal scarring.
For those seeking expert care in Manhattan, contact the experienced team at Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery to schedule a consultation and discuss the most effective surgical options for your soft tissue and skin health.
Contact Information
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY PLLC
Dr. Valery Dronsky
117 E 77th Street
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
admin@lenoxmis.com
Minimally Invasive Techniques in General Surgery: Advantages and Benefits
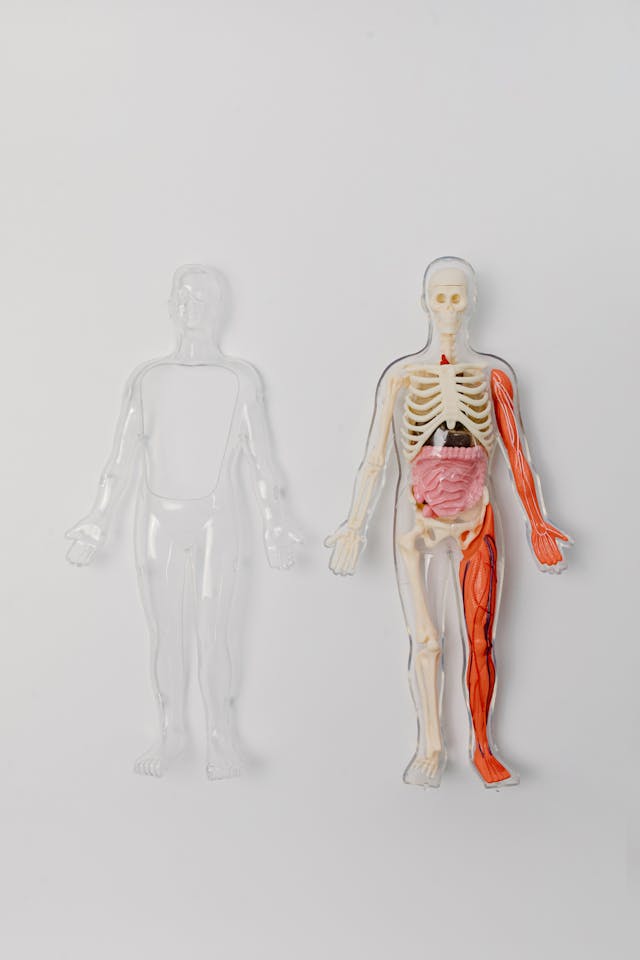 In this guide, we’ll explore what minimally invasive techniques in general surgery involves, the key advantages for patients, and the types of conditions commonly treated using these advanced methods.
In this guide, we’ll explore what minimally invasive techniques in general surgery involves, the key advantages for patients, and the types of conditions commonly treated using these advanced methods.
Minimally invasive surgery has transformed the field of general surgery, offering patients an effective way to address various health conditions with reduced pain, quicker recovery, and minimal scarring. This approach relies on advanced surgical technology, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions rather than the larger cuts used in traditional surgery. Today, minimally invasive techniques are applied in a wide range of procedures, including hernia repair, gallbladder removal, colorectal surgery, and many others.
What is Minimally Invasive Surgery?
Minimally invasive surgery involves performing surgical procedures through small incisions using specialized tools and imaging technology. Instead of making a large incision to access the surgical site, surgeons use instruments such as laparoscopes or robotic systems to view and operate on internal organs. A laparoscope is a thin tube with a camera that allows the surgeon to see inside the body, while robotic systems provide enhanced precision, control, and flexibility.
The two primary types of minimally invasive surgery are:
- Laparoscopic Surgery: This technique uses a laparoscope, which is inserted through small incisions to provide a clear view of the surgical site. The surgeon performs the operation using small, specialized instruments.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Robotic systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, allow surgeons to perform procedures with greater precision and control. The surgeon operates the robotic arms from a console, which enhances accuracy, particularly in delicate and complex surgeries.
Advantages of Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery offers several benefits over traditional open surgery, making it an attractive option for many patients. Here are some of the primary advantages:
- Smaller Incisions and Minimal Scarring: Minimally invasive techniques require only small incisions, typically around 1-2 centimeters, as opposed to larger incisions in traditional surgery. This results in less visible scarring, which can improve physical and psychological recovery.
- Reduced Pain and Discomfort: Smaller incisions mean less trauma to the body, resulting in reduced pain during and after surgery. Patients typically require fewer pain medications post-operatively, which contributes to a smoother recovery process.
- Faster Recovery Time: Patients undergoing minimally invasive surgery generally experience a quicker recovery than those who have traditional open surgery. This allows them to return to daily activities and work sooner, reducing the overall impact on their lifestyle.
- Shorter Hospital Stays: Minimally invasive surgery often requires a shorter hospital stay, with many patients able to go home the same day or within 1-2 days. This lowers healthcare costs and minimizes the risk of hospital-acquired infections.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Due to the smaller incisions and reduced tissue trauma, minimally invasive surgery is associated with a lower risk of complications such as infections, blood loss, and post-operative complications.
- Improved Precision: Robotic-assisted surgery, in particular, enhances the surgeon’s precision and control. This is especially beneficial for complex procedures, allowing for more accurate results and better outcomes for patients.
Conditions Commonly Treated with Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive techniques are used to treat a wide range of conditions across various specialties in general surgery. Some of the most common conditions treated with minimally invasive surgery include:
1. Gallbladder Disease
Minimally invasive surgery, such as laparoscopic cholecystectomy, is the preferred method for removing the gallbladder when treating gallbladder disease, including gallstones and cholecystitis. This procedure involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope to guide the removal of the gallbladder, resulting in less pain and faster recovery compared to open surgery.
2. Hernia Repair
Hernia repair can be effectively performed using minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic hernia repair or robotic-assisted hernia repair. These methods allow surgeons to reinforce the weakened area with mesh through small incisions, reducing the risk of recurrence and promoting quicker healing.
3. Colorectal Surgery
Conditions such as diverticulitis, colorectal cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may require colorectal surgery. Minimally invasive approaches, including laparoscopic and robotic-assisted colorectal surgery, allow for precise removal of diseased sections of the colon or rectum with minimal impact on surrounding tissue.
4. Appendectomy
For cases of appendicitis, a laparoscopic appendectomy is often used to remove the inflamed appendix. This minimally invasive technique provides faster recovery and reduced pain, enabling patients to return to their daily routines quickly.
5. Bariatric (Weight Loss) Surgery
Bariatric surgery, such as laparoscopic gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, is commonly performed to treat obesity and related health conditions. Minimally invasive bariatric surgery allows for effective weight loss with smaller incisions, less post-operative pain, and a shorter recovery period.
6. Anti-Reflux Surgery (GERD)
For severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a minimally invasive procedure called laparoscopic fundoplication can be used to prevent acid reflux. This involves wrapping the top of the stomach around the lower esophagus to strengthen the valve and reduce acid reflux symptoms.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Enhancing Precision and Control
Robotic-assisted surgery is a form of minimally invasive surgery that offers even greater precision, control, and flexibility. During robotic-assisted procedures, the surgeon operates robotic arms that can mimic the movements of the human wrist, allowing for complex maneuvers that are difficult to achieve with traditional laparoscopy. The benefits of robotic-assisted surgery include:
- Increased Dexterity: Robotic systems provide enhanced control and flexibility, allowing surgeons to perform intricate movements and access hard-to-reach areas.
- Enhanced Visualization: Robotic systems provide high-definition, 3D visualization, allowing surgeons to view the surgical site in great detail, improving accuracy and safety.
- Reduced Tremor: Robotic systems minimize natural hand tremors, providing smooth and precise movements during surgery.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care After Minimally Invasive Surgery
Recovery after minimally invasive surgery is generally faster and less painful than recovery from traditional open surgery. Here’s what most patients can expect:
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Many minimally invasive surgeries are outpatient procedures or require only a short hospital stay, allowing patients to return home sooner.
- Less Post-Operative Pain: Patients typically experience less pain, reducing the need for pain medications and contributing to a more comfortable recovery.
- Quick Return to Activities: Patients can usually resume light activities within a few days and gradually return to their regular routines, including work, within a few weeks.
- Reduced Scarring: Small incisions result in minimal scarring, which can be beneficial for both physical recovery and self-esteem.
Minimally Invasive Techniques in General Surgery: Conclusion
Minimally invasive surgery has revolutionized general surgery, providing patients with safer, more comfortable, and quicker treatment options. If you have been diagnosed with a condition that may require surgery, consult with a general surgeon to discuss whether a minimally invasive approach is suitable for your case. With the latest advancements in surgical technology, many procedures that once required open surgery can now be performed with minimally invasive techniques, offering better outcomes and faster recovery.
For those in Manhattan seeking expert general surgical care, the team at Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery specializes in minimally invasive techniques, providing patients with compassionate, high-quality care. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn more about how minimally invasive surgery can benefit you.
Contact Information
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
117 E 77th Street
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
admin@lenoxmis.com
Visit our website for more information: https://lenoxhillminimallyinvasivesurgery.com/
Spleen Surgery: Surgical Interventions for Splenic Conditions
In this guide, we’ll explore common splenic conditions that may require surgery, the types of surgical interventions available, and what patients can expect during recovery.
The spleen is an important organ located in the upper left side of the abdomen. It plays a crucial role in filtering blood, fighting infections, and managing blood cells. Although the spleen is essential for immune function, certain conditions and injuries may require surgical intervention to remove or repair the spleen. Spleen surgery, or splenectomy, can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life, especially when the organ’s dysfunction or damage leads to other health complications.
Common Conditions Requiring Spleen Surgery
There are several conditions and situations where spleen surgery may be necessary. Here are some of the most common reasons for surgical intervention:
1. Splenic Rupture
A ruptured spleen is often the result of trauma, such as a car accident or a severe fall. A ruptured spleen can cause internal bleeding and is a medical emergency. Surgery may be required to remove or repair the spleen, depending on the extent of the injury.
2. Splenomegaly (Enlarged Spleen)
Splenomegaly is a condition where the spleen becomes enlarged, often due to infections, liver disease, blood disorders, or certain cancers. An enlarged spleen may cause pain, fatigue, and an increased risk of rupture. If the spleen is severely enlarged and causes symptoms, a splenectomy may be recommended.
3. Hematologic Disorders
Certain blood disorders, such as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), thalassemia, and hereditary spherocytosis, affect the function of the spleen. In some cases, removing the spleen can help manage these disorders by improving blood cell counts or reducing symptoms.
4. Spleen Cysts and Tumors
Although rare, cysts and tumors can develop in the spleen. These growths may be benign or malignant, and large or symptomatic cysts or tumors may require surgical removal. A partial splenectomy may be performed if only a part of the spleen is affected.
5. Sickle Cell Disease
In patients with sickle cell disease, the spleen may become damaged over time due to the abnormal shape of red blood cells. This can lead to a condition known as autosplenectomy, where the spleen shrinks and loses function. In some cases, surgical removal of the damaged spleen may be necessary to prevent further complications.
Types of Spleen Surgery
The type of surgery performed on the spleen depends on the underlying condition and the extent of damage. Here are the primary types of splenic surgery:
- Splenectomy: A splenectomy is the complete removal of the spleen. It is commonly performed in cases of trauma, certain blood disorders, and when the spleen is severely enlarged or damaged. After a splenectomy, the body can still function without the spleen, but patients may need vaccinations and preventive measures to reduce the risk of infections.
- Partial Splenectomy: In some cases, only part of the spleen is removed, allowing the patient to retain some splenic function. This is often considered for patients with localized cysts, tumors, or partial trauma. A partial splenectomy preserves some immune function and reduces the risk of infection.
- Splenic Artery Embolization: Splenic artery embolization is a less invasive procedure that involves blocking the blood supply to the spleen, causing part of it to shrink. This technique can be used to treat splenic trauma or reduce spleen size in certain hematologic conditions, and may be performed as an alternative to full splenectomy.
- Laparoscopic Splenectomy: Laparoscopic splenectomy is a minimally invasive technique used to remove the spleen through small incisions. Using a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) and specialized instruments, the surgeon can perform the splenectomy with minimal trauma to surrounding tissues. Laparoscopic splenectomy is often preferred due to its faster recovery time and reduced post-operative pain.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Spleen Surgery
When possible, minimally invasive spleen surgery, such as laparoscopic splenectomy, is preferred over traditional open surgery. Minimally invasive surgery offers several benefits:
- Reduced Pain: Smaller incisions mean less trauma to the body, leading to less post-operative pain.
- Faster Recovery: Patients who undergo laparoscopic procedures often experience a quicker recovery and shorter hospital stay.
- Lower Risk of Infection: The risk of infection is reduced due to smaller incisions and less tissue disruption.
- Minimal Scarring: Small incisions result in less visible scarring, which can improve physical and psychological recovery.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Recovery from spleen surgery depends on the type of procedure performed and the individual’s overall health. Here’s what patients can generally expect during the recovery period:
- Hospital Stay: After a laparoscopic splenectomy, most patients can go home within a few days. However, open surgery may require a longer hospital stay for observation and pain management.
- Pain Management: Pain is common after spleen surgery, especially with open procedures. Pain management techniques include prescribed medications and following post-operative care instructions.
- Physical Activity: Light physical activity, such as walking, is encouraged after surgery to prevent blood clots and improve circulation. However, strenuous activities and heavy lifting should be avoided for several weeks to prevent complications.
- Risk of Infection: Since the spleen plays an important role in the immune system, patients who undergo a splenectomy have a higher risk of infection. It’s essential for these patients to receive vaccinations and may require preventive antibiotics.
- Dietary Adjustments: There are usually no specific dietary restrictions after spleen surgery, but following a balanced diet can support healing and recovery.
Improving Quality of Life through Spleen Surgery
For many patients with chronic spleen-related conditions, surgery can significantly improve quality of life. Removing or partially removing the spleen can help alleviate symptoms, prevent future health risks, and allow patients to resume their daily activities without discomfort. Patients with hematologic disorders, for example, may experience more stable blood cell counts and reduced symptoms after a splenectomy.
While living without a spleen requires some lifestyle adjustments and preventive health measures, the overall impact on daily life can be positive. Many patients experience long-term relief from symptoms and complications, leading to improved physical and mental well-being.

When to Consider Spleen Surgery
If you have a splenic condition that affects your quality of life or poses a health risk, spleen surgery may be an appropriate option. Consulting with an experienced general surgeon who specializes in splenic conditions can help you understand the benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of surgery. Early intervention can often prevent complications and lead to better outcomes.
For those seeking expert splenic surgery in Manhattan, the team at Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery provides compassionate, specialized care for a wide range of splenic conditions. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn more about the advanced surgical options available to help you achieve optimal health.
Contact Information
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY PLLC
117 E 77th Street
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
admin@lenoxmis.com
Visit our website for more information: https://lenoxhillminimallyinvasivesurgery.com/
General Surgery For Gastrointestinal Conditions
 In this guide, we’ll explore common gastrointestinal conditions that may require surgery, the types of surgeries used to treat them, and the positive impact these procedures can have on patients’ lives.
In this guide, we’ll explore common gastrointestinal conditions that may require surgery, the types of surgeries used to treat them, and the positive impact these procedures can have on patients’ lives.
Gastrointestinal (GI) conditions encompass a wide range of disorders that affect the digestive system, including the stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. For many people, these conditions can cause significant discomfort, nutritional deficiencies, and impact overall quality of life. While some gastrointestinal conditions can be managed through lifestyle changes, medications, and other non-surgical treatments, surgery may be the most effective solution in certain cases, especially when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief.
Common Gastrointestinal Conditions Treated with Surgery
There are various GI conditions for which surgery can be a highly effective treatment. Below are some of the most common gastrointestinal disorders that may require surgical management:
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is a chronic condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort, heartburn, and potential damage to the esophageal lining. For severe cases of GERD that don’t respond to medication and lifestyle changes, a procedure known as fundoplication may be recommended. In this procedure, the top of the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophagus to prevent acid reflux.
2. Gallbladder Disease
Gallbladder disease, particularly gallstones, can lead to severe pain and inflammation. Gallstones can block the bile ducts, causing cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) and increasing the risk of infection. A cholecystectomy, or gallbladder removal surgery, is often the best treatment to prevent recurrent symptoms and complications from gallstones.
3. Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis occurs when small pouches (diverticula) in the colon become inflamed or infected. For patients with recurrent or severe diverticulitis, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected part of the colon and reduce the risk of future episodes.
4. Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are types of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that cause chronic inflammation in the digestive tract. In severe cases where medications are not effective, surgery may be required to remove the diseased sections of the intestines. Bowel resection and colectomy are common surgical procedures used to manage these conditions.
5. Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment. Surgery is often the primary treatment for localized colorectal cancer, with procedures like colon resection or colectomy performed to remove cancerous parts of the colon or rectum. Early detection and surgical intervention can improve outcomes and reduce the risk of cancer spreading.
6. Small Bowel Obstruction
A small bowel obstruction can occur due to adhesions, tumors, hernias, or other factors that block the passage of food and fluids through the intestines. When conservative treatments fail, surgery may be required to remove the blockage and restore normal function.
Surgical Procedures for Gastrointestinal Conditions
The type of surgical procedure recommended will depend on the specific gastrointestinal condition, its severity, and the patient’s overall health. Here are some of the most common GI surgeries:
- Fundoplication: A procedure primarily used to treat GERD, where the upper part of the stomach is wrapped around the esophagus to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter and prevent acid reflux.
- Cholecystectomy: Gallbladder removal surgery used to treat gallbladder disease, especially in cases of recurrent gallstones or inflammation.
- Colectomy: A surgical procedure to remove all or part of the colon. It is often performed for conditions like diverticulitis, colorectal cancer, or severe inflammatory bowel disease.
- Resection with Anastomosis: In this procedure, the diseased part of the intestine is removed, and the healthy ends are reconnected, ensuring continuity of the digestive tract. This is common in cases of Crohn’s disease, colon cancer, and small bowel obstructions.
- Ostomy Creation: An ostomy is a surgically created opening in the abdomen to allow waste to exit the body, bypassing the affected area of the digestive tract. Ostomies, such as colostomies and ileostomies, are used when parts of the bowel need to be bypassed due to disease.
- Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): A minimally invasive procedure that removes abnormal or cancerous tissue from the lining of the digestive tract. It is often used for early-stage cancers or pre-cancerous lesions in the esophagus, stomach, or intestines.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Surgery for GI Conditions
Advancements in surgical technology have led to the development of minimally invasive techniques, including laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery. These approaches allow surgeons to perform complex GI surgeries with smaller incisions and greater precision. Benefits of minimally invasive surgery include:
- Reduced Pain: Smaller incisions cause less trauma to the body, resulting in less post-operative pain.
- Faster Recovery: Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays and quicker return to daily activities.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Minimally invasive techniques reduce the risk of infection and other complications.
- Minimal Scarring: Small incisions lead to less visible scarring, which can improve physical and emotional recovery.
Recovery After Gastrointestinal Surgery
Recovery after gastrointestinal surgery depends on the specific procedure performed and the patient’s overall health. Here’s what most patients can expect during recovery:
- Hospital Stay: Minimally invasive procedures often require a shorter hospital stay, while more extensive surgeries may require longer observation and care.
- Dietary Adjustments: Patients may need to follow a special diet after surgery, starting with liquids and gradually progressing to solid foods. A nutritionist may provide guidance to ensure a balanced diet that supports healing.
- Pain Management: Post-operative pain is managed with prescribed medications, and patients are encouraged to follow their surgeon’s instructions for comfort.
- Physical Activity: Light physical activity, such as walking, is encouraged soon after surgery to promote circulation and prevent blood clots. However, heavy lifting and strenuous activities should be avoided until cleared by the surgeon.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, manage symptoms, and address any complications that may arise.

Improving Quality of Life through GI Surgery
For individuals suffering from chronic GI conditions, surgery can be transformative. Many patients experience significant improvements in their quality of life after successful surgical treatment. By addressing the root cause of pain, discomfort, and other symptoms, surgery can help restore normal digestion, reduce pain, and improve overall physical and mental well-being.
Some success stories include patients who have regained their ability to enjoy food, participate in physical activities, and lead a more comfortable life post-surgery. Early intervention and choosing a skilled surgical team are key to achieving the best possible outcomes.
General Surgery For Gastrointestinal Conditions: Conclusion
If you’re dealing with a gastrointestinal condition that doesn’t respond to medications or other treatments, surgery may be a viable option to improve your quality of life. Consulting with a general surgeon who specializes in GI conditions can help you understand the most effective treatment options based on your unique case and overall health.
For those in Manhattan seeking expert surgical solutions for gastrointestinal conditions, the team at Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery is here to provide comprehensive, patient-centered care. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn how advanced surgical techniques can help you regain control of your health and well-being.
Contact Information
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY PLLC
Dr. Valery Dronsky
117 E 77th Street
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
dr.dronsky@lenoxmis.com
Visit our website for more information:
www.lenoxhillminimallyinvasivesurgery.com/
Small Intestine Surgery: Treatment Options for Intestinal Disorders
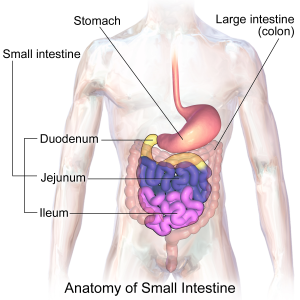 This comprehensive guide explores common small intestine disorders that may necessitate surgery, the types of surgical treatments available, and what patients can expect during the recovery process.
This comprehensive guide explores common small intestine disorders that may necessitate surgery, the types of surgical treatments available, and what patients can expect during the recovery process.
The small intestine is a crucial part of the digestive system, responsible for absorbing nutrients from food and facilitating digestion. However, certain conditions and disorders can affect the small intestine, leading to discomfort, nutrient malabsorption, and other health complications. When non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be required to address the underlying issue.
Common Small Intestine Disorders Requiring Surgery
There are various disorders affecting the small intestine that may require surgical intervention. Here are some of the most common conditions:
1. Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, often affecting the small intestine. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and malnutrition. In severe cases where medications and other treatments do not control symptoms, surgery may be necessary to remove diseased sections of the intestine.
2. Small Bowel Obstruction
A small bowel obstruction is a blockage that prevents food and fluids from passing through the small intestine. This can be caused by adhesions from previous surgeries, hernias, tumors, or other conditions. When conservative treatments, such as nasogastric decompression, are ineffective, surgery may be required to relieve the obstruction.
3. Small Intestinal Tumors
Benign or malignant tumors can develop in the small intestine. While benign tumors may be removed to alleviate symptoms, malignant tumors require surgical resection to prevent cancer from spreading. Early intervention is key to achieving better outcomes.
4. Diverticulitis of the Small Intestine
Although diverticulitis is more commonly associated with the colon, it can also occur in the small intestine. Diverticulitis is an inflammation or infection of small pouches (diverticula) that can form in the intestinal wall. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected portion of the intestine and prevent recurrent infections.
5. Intestinal Ischemia
Intestinal ischemia occurs when there is a loss of blood flow to the small intestine, leading to tissue damage. This condition can be life-threatening and often requires immediate surgical intervention to remove the damaged section of the intestine and restore blood flow.
Surgical Options for Small Intestine Disorders
Depending on the specific condition affecting the small intestine, several surgical options are available to manage and treat the disorder. Here are some of the most common surgical procedures:
- Small Bowel Resection: This procedure involves removing the diseased or blocked part of the small intestine and reconnecting the healthy ends. Small bowel resection is commonly used to treat Crohn’s disease, obstructions, and tumors.
- Strictureplasty: Strictureplasty is used to treat strictures, or narrowing of the intestine, commonly seen in Crohn’s disease. Instead of removing the narrowed section, the surgeon widens it, allowing for normal food passage while preserving more of the intestine.
- Enterostomy: Enterostomy involves creating an opening (stoma) in the small intestine to divert waste. This may be necessary in cases where a part of the intestine needs to be bypassed or if a temporary opening is needed for healing after surgery.
- Intestinal Bypass: This procedure is used less commonly but may be performed to bypass a diseased or obstructed part of the small intestine, especially when resection isn’t possible. It can help restore normal digestion.
- Segmental Resection with Anastomosis: In this procedure, a diseased segment of the small intestine is removed, and the healthy ends are reconnected, or “anastomosed,” to ensure continuity of the digestive tract. This is often used for tumors and specific cases of Crohn’s disease.
Minimally Invasive Approaches in Small Intestine Surgery
Many small intestine surgeries can now be performed using minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery. These techniques offer several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
- Reduced Recovery Time: Minimally invasive surgery typically allows for faster healing, helping patients return to daily activities sooner.
- Less Post-Operative Pain: Smaller incisions mean less trauma to the body, resulting in reduced pain following surgery.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Minimally invasive techniques are associated with a lower risk of infection and complications.
- Minimal Scarring: Small incisions result in less visible scarring, which can improve both physical and psychological recovery.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Recovery from small intestine surgery varies depending on the specific procedure and the patient’s overall health. Here’s what most patients can expect during the recovery period:
- Hospital Stay: Small intestine surgeries generally require a hospital stay of a few days, especially if a bowel resection is involved. Patients are monitored for complications, such as infection or bleeding, and receive nutritional support if needed.
- Dietary Adjustments: Following surgery, patients may start with a liquid diet, gradually moving to soft foods before reintroducing regular foods. A nutritionist may provide guidance on maintaining a balanced diet for optimal healing and digestion.
- Pain Management: Pain after surgery is managed with prescribed medications, and patients are encouraged to follow all post-operative instructions to ensure comfort and reduce complications.
- Physical Activity: Light physical activity, such as walking, is encouraged soon after surgery to prevent blood clots and improve circulation. However, strenuous activities should be avoided until cleared by the surgeon.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor healing, ensure proper digestive function, and address any potential complications.
When to Consider Small Intestine Surgery
Surgery for small intestine disorders is typically considered when other treatment options have failed or when the condition poses a serious health risk. If you have a small intestine disorder and are not finding relief from medication or lifestyle changes, consult a general surgeon specializing in digestive health to discuss your options. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve outcomes, helping you achieve a better quality of life.
If you’re in Manhattan and seeking expert surgical treatment for small intestine disorders, reach out to the experienced team at Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn more about our advanced surgical techniques and patient-centered approach to care.
Contact Information
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY PLLC
Dr. Valery Dronsky
117 E 77th Street
Suite 1A
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
dr.dronsky@lenoxmis.com
Visit our website for more information:
www.lenoxhillminimallyinvasivesurgery.com/
General Surgery To Manage Chronic Pain?
Cqn general surgery be used to manage chronic pain? Having constant pain can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, affecting everything from mobility and sleep to mental health and daily functioning. While many individuals turn to medication, physical therapy, and other non-surgical options to manage pain, there are certain conditions where general surgery offers an effective, long-term solution. General surgeons play a crucial role in treating the underlying causes of pain, providing patients with relief and helping them return to their normal activities.

Chronic Pain Conditions Commonly Treated with General Surgery
Some pain conditions are best managed through surgery, especially when conservative treatments have not provided sufficient relief. Here are some common pain-related conditions that may be treated effectively with surgical intervention:
1. Herniated Discs
A herniated disc occurs when one of the discs in the spine ruptures or slips out of place, often putting pressure on nearby nerves. This can lead to chronic back and leg pain, numbness, and weakness. When non-surgical treatments fail to relieve symptoms, surgery, such as a microdiscectomy or spinal fusion, may be necessary to alleviate the pain.
2. Chronic Joint Pain (Arthritis)
Arthritis, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees, can cause severe pain and limit mobility. For individuals with advanced arthritis who do not respond to medications or physical therapy, joint replacement surgery may be the most effective way to restore function and relieve pain.
3. Gallstones and Gallbladder Disease
Gallstones can block the bile ducts, leading to intense abdominal pain, inflammation, and even infection. For individuals with recurrent gallbladder pain or complications from gallstones, a cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal surgery) is often recommended.
4. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve in the wrist becomes compressed, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness in the hand and fingers. Carpal tunnel release surgery can relieve pressure on the nerve, providing long-term relief from symptoms.
5. Peripheral Nerve Compression
Certain conditions, such as thoracic outlet syndrome, can cause compression of peripheral nerves, resulting in chronic pain in the arms, shoulders, or neck. Nerve decompression surgery can help relieve the pressure on these nerves and reduce pain.
Surgical Procedures for Pain Relief
There are a variety of surgical procedures that general surgeons use to manage chronic pain effectively. The choice of surgery depends on the underlying cause of the pain and the patient’s overall health. Here are some of the most common surgical options:
- Microdiscectomy: A minimally invasive procedure used to treat herniated discs, where only the portion of the disc pressing on the nerve is removed.
- Spinal Fusion: A procedure where two or more vertebrae are permanently joined together to stabilize the spine and relieve pain from degenerative conditions.
- Joint Replacement: Often used for hip and knee arthritis, joint replacement surgery involves removing damaged joint surfaces and replacing them with prosthetic components to restore function and alleviate pain.
- Cholecystectomy: This procedure involves the removal of the gallbladder to prevent the recurrence of gallstone-related pain and complications.
- Carpal Tunnel Release: A surgical procedure where the ligament in the wrist is cut to relieve pressure on the median nerve, reducing pain and restoring hand function.
- Nerve Decompression Surgery: Used to alleviate pressure on peripheral nerves, this surgery can help relieve chronic pain from conditions like thoracic outlet syndrome.
Advances in Minimally Invasive Surgery for Pain Management
Advances in minimally invasive surgical techniques have made pain management surgeries more accessible and effective. Many procedures that once required large incisions can now be performed with minimal tissue disruption, resulting in several benefits for patients.
- Reduced Recovery Time: Minimally invasive surgery generally allows for faster healing and shorter hospital stays.
- Less Post-Operative Pain: Smaller incisions mean less trauma to the body, leading to less pain following surgery.
- Lower Risk of Complications: The risk of infection and other complications is reduced with minimally invasive procedures.
- Minimal Scarring: Small incisions result in less visible scarring, which can be beneficial for both physical and psychological recovery.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
The recovery process after pain management surgery varies depending on the type of procedure performed and the patient’s overall health. Here’s what most patients can expect during their recovery:
- Pain Management: Pain is common after surgery, and most patients are provided with medications and pain management strategies to help alleviate discomfort during the recovery period.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is often recommended to help patients regain strength and mobility after surgery, particularly for joint replacements and spinal surgeries.
- Dietary Adjustments: For certain surgeries, like gallbladder removal, dietary adjustments may be necessary to aid in digestion and reduce symptoms.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor healing and address any complications.
Success Stories: How Surgery Has Changed Lives
Many patients have experienced life-changing results from surgery to manage chronic pain. Here are a few examples of success stories:
- A patient with a herniated disc that caused severe sciatic pain found complete relief after a microdiscectomy, allowing them to return to work and regular physical activities.
- An older adult suffering from chronic knee pain and limited mobility due to arthritis underwent a knee replacement and now enjoys a pain-free life with improved mobility.
- A young professional dealing with intense wrist pain and hand numbness due to carpal tunnel syndrome achieved full recovery and regained hand function following carpal tunnel release surgery.
General Surgery to Manage Chronic Pain: When to Consider Surgery for Pain Management
If you are struggling with chronic pain that is not responding to conservative treatments, surgery may be a viable option to help you regain control of your life. Consulting with a skilled general surgeon who specializes in pain management can help determine the most effective approach based on your condition and overall health. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes and improve your quality of life.
For those seeking expert general surgical solutions for pain management in Manhattan, consider consulting with the experienced team at Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and discuss how our advanced surgical techniques can provide you with lasting relief from chronic pain.
Contact Information
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
117 E 77th Street
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
admin@lenoxmis.com
Visit our website for more information: https://lenoxhillminimallyinvasivesurgery.com/
Pancreas Surgery: Management of Pancreatic Diseases through Surgery
When is pancreas surgery necessary? The pancreas is a vital organ located behind the stomach, responsible for producing digestive enzymes and regulating blood sugar through hormone production. When pancreatic diseases occur, they can have severe consequences on overall health. For conditions that cannot be managed through medication or lifestyle changes, pancreas surgery often becomes a necessary treatment option.

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore common pancreatic diseases that may require surgery, the different types of pancreatic surgeries, the latest advancements in surgical techniques, and what patients can expect during recovery.
Common Pancreatic Diseases Requiring Surgery
Several conditions affecting the pancreas may necessitate surgical intervention. Here are some of the most common pancreatic diseases that often require surgical management:
1. Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most serious forms of cancer, often diagnosed at an advanced stage due to its subtle symptoms. The most common type is pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, which typically originates in the ducts of the pancreas. Surgery is a primary treatment for pancreatic cancer, especially if it’s localized and detected early.
2. Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is the inflammation of the pancreas, which can be acute or chronic. Acute pancreatitis is usually a sudden condition that may resolve with conservative treatment, while chronic pancreatitis is a long-term, progressive inflammation often due to repeated bouts of acute pancreatitis, gallstones, or alcohol use. Surgery may be recommended for chronic pancreatitis when there’s persistent pain, blockage, or other complications.
3. Pancreatic Cysts and Neoplasms
Pancreatic cysts and benign neoplasms are growths in the pancreas. While many pancreatic cysts are benign, some have the potential to become cancerous over time. Surgery may be required to remove cysts if they are symptomatic, large, or carry a risk of malignancy.
4. Neuroendocrine Tumors
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are a rare type of tumor that originates in the hormone-producing cells of the pancreas. These tumors can be either benign or malignant and may produce symptoms related to excess hormone production. Surgery is often the first line of treatment, especially if the tumor is localized and can be safely removed.
Types of Pancreatic Surgery
The type of surgery performed on the pancreas depends on the specific disease, its location, and the stage at which it is diagnosed. Here are some of the most common pancreatic surgical procedures:
1. Whipple Procedure (Pancreaticoduodenectomy)
The Whipple procedure, or pancreaticoduodenectomy, is the most common surgery for pancreatic cancer located in the head of the pancreas. During this complex procedure, the surgeon removes the head of the pancreas, part of the small intestine (duodenum), the gallbladder, and sometimes part of the stomach. The remaining organs are then reconnected to allow for normal digestion. Although it is a major surgery, the Whipple procedure is often the best option for treating cancers in the head of the pancreas.
2. Distal Pancreatectomy
In a distal pancreatectomy, the tail (and sometimes part of the body) of the pancreas is removed, leaving the head intact. This procedure is commonly performed for tumors or cysts located in the tail of the pancreas. In some cases, the spleen may also be removed if it is affected or if it will facilitate a safer procedure.
3. Total Pancreatectomy
A total pancreatectomy involves the removal of the entire pancreas. This procedure is usually reserved for cases where cancer or disease affects the entire pancreas and cannot be treated by removing only part of the organ. After a total pancreatectomy, the patient will require lifelong enzyme replacement and insulin therapy, as the body will no longer be able to produce insulin or digestive enzymes.
4. Enucleation
Enucleation is a less invasive procedure often used to remove small, benign pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. During enucleation, only the tumor is removed, preserving as much of the healthy pancreas tissue as possible. This procedure is ideal for small, well-defined tumors that do not invade nearby structures.
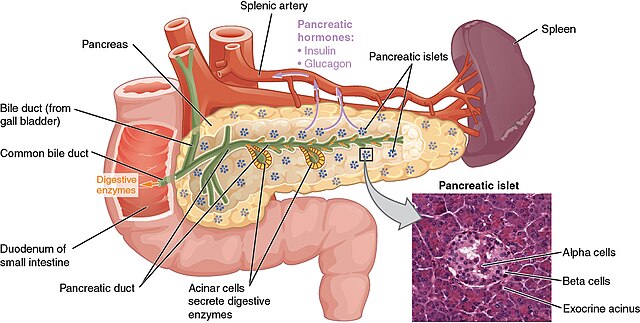
Advances in Minimally Invasive Pancreatic Surgery
Recent advancements in surgical technology have made minimally invasive approaches more accessible and effective for pancreatic surgery. Minimally invasive techniques, including **laparoscopic** and **robotic-assisted surgery**, offer patients significant benefits compared to traditional open surgery.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive approach uses small incisions and a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) to guide the surgery. Surgeons can perform complex pancreatic procedures with greater precision and minimal trauma to surrounding tissues.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Robotic-assisted surgery enhances the surgeon’s dexterity and control, allowing for more precise movements in delicate areas. This approach is especially beneficial for complex procedures, as it reduces the likelihood of complications and often results in faster recovery times.
The benefits of minimally invasive pancreatic surgery include:
- Smaller incisions and less scarring
- Reduced post-operative pain
- Shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times
- Lower risk of infection and complications
Recovery After Pancreatic Surgery
Recovery from pancreatic surgery depends on the type of procedure performed and the patient’s overall health. Here’s what most patients can expect during recovery:
- Hospital Stay: Pancreatic surgeries are major procedures, often requiring a hospital stay ranging from a few days to two weeks, depending on the complexity of the surgery and any complications.
- Pain Management: Pain is common after pancreatic surgery, especially with open procedures. Pain management techniques include medications and, in some cases, epidural or nerve block anesthesia for the first few days.
- Dietary Adjustments: After surgery, patients will need to follow a special diet to allow the pancreas to heal. This usually starts with a liquid diet, followed by soft foods. Patients may also require enzyme supplements to aid in digestion, especially if a large part of the pancreas was removed.
- Lifelong Management: For patients who undergo a total pancreatectomy, lifelong enzyme replacement and insulin therapy are necessary. Even with partial removal, patients may need ongoing management to control blood sugar levels and support digestion.
Success Stories and Improvements in Quality of Life
Pancreatic surgery can be life-changing for patients dealing with chronic pain, cancer, or other debilitating symptoms due to pancreatic diseases. Success stories often highlight patients who have regained control of their health, with significantly improved quality of life. Some individuals with pancreatic cancer have been able to achieve remission through early intervention and surgery, while others suffering from chronic pancreatitis have been able to live pain-free after successful surgical treatment.
The improvements in minimally invasive techniques and post-operative care have increased the success rates of pancreatic surgeries, allowing patients to enjoy better outcomes and faster recovery times.
When to Consider Pancreas Surgery
Patients diagnosed with serious pancreatic conditions should consider surgery as a treatment option if recommended by their healthcare provider. Early intervention is key for the best outcomes, particularly in cases of pancreatic cancer or neuroendocrine tumors. Discussing the benefits, risks, and long-term impacts of surgery with a general surgeon specializing in pancreatic diseases can help you make an informed decision about your treatment plan.
If you or a loved one is facing a pancreatic disorder that may require surgery, consulting with a team of skilled surgeons can make all the difference in your recovery journey.
Contact Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery today to schedule a consultation and learn more about the latest advancements in pancreatic surgery and how our experienced team can help you on the path to restored health.
Contact Information
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
117 E 77th Street
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
admin@lenoxmis.com
Visit our website for more information: https://lenoxhillminimallyinvasivesurgery.com/
The Role of General Surgery in Cancer Treatment: Latest Approaches
General surgery plays a vital role in the treatment of various types of cancer, often serving as the primary or first-line treatment for many solid tumors. With the rapid advancements in surgical techniques and technology, the field of general surgery has become increasingly effective in addressing cancerous growths, minimizing patient discomfort, and enhancing recovery. For those facing a cancer diagnosis, understanding the role of general surgery and the latest approaches available can empower patients and their families to make informed decisions.
This guide will explore how general surgery is used in cancer treatment, the latest surgical approaches, and the benefits of minimally invasive techniques.
Understanding the Role of General Surgery in Cancer Treatment
Surgery is often one of the primary treatments for cancer, particularly when the cancer is localized and has not spread to other parts of the body. Surgery can serve several purposes in the treatment of cancer:
- Curative Surgery: When the entire tumor can be removed, surgery may offer a potential cure for certain cancers. Curative surgery is most effective when cancer is detected early and remains localized.
- Debulking Surgery: In cases where removing the entire tumor is not possible or safe, debulking surgery may be performed to reduce the size of the tumor. This can help improve the effectiveness of other treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation.
- Palliative Surgery: For advanced cancers, surgery may be used to relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life, even if the cancer itself cannot be cured.
- Preventive Surgery: For individuals at high risk of certain cancers, preventive (or prophylactic) surgery may be performed to remove tissue that is likely to become cancerous in the future.
The surgical approach depends on the type, stage, and location of cancer, as well as the overall health of the patient.
Latest Surgical Approaches in Cancer Treatment
With advances in technology and surgical techniques, the treatment of cancer has evolved significantly. Here are some of the latest and most effective approaches in surgical oncology:
1. Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS)
Minimally invasive surgery, including laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery, has revolutionized the field of cancer surgery. Using small incisions, high-definition cameras, and precise instruments, surgeons can perform complex procedures with greater accuracy and less trauma to surrounding tissues.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: This technique uses a laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera, inserted through a small incision. The surgeon views a magnified image on a screen and operates through additional small incisions. Laparoscopic surgery is commonly used for cancers of the colon, stomach, liver, and pancreas.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: With robotic-assisted systems like the da Vinci Surgical System, surgeons can operate with enhanced dexterity and control. This is particularly beneficial for cancers in hard-to-reach areas, such as prostate or rectal cancer.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Surgery:
- Smaller incisions and minimal scarring
- Reduced blood loss
- Shorter hospital stays
- Faster recovery times
- Lower risk of infection and complications
2. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
In cancers such as breast cancer and melanoma, determining whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes is essential for staging and treatment planning. A sentinel lymph node biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure that identifies the first lymph node to which cancer cells are likely to spread. By targeting only the sentinel node, this approach reduces the need for extensive lymph node removal, decreasing the risk of complications like lymphedema.
3. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) and Microwave Ablation (MWA)
For small tumors, especially in the liver, kidneys, and lungs, radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA) are effective alternatives to traditional surgery. These treatments use heat generated by radio waves or microwaves to destroy cancer cells. RFA and MWA are minimally invasive and can be performed using image guidance without large incisions.
4. Cryosurgery
Cryosurgery, also known as cryotherapy, uses extreme cold to destroy cancerous tissue. Liquid nitrogen or argon gas is applied directly to the tumor, freezing and killing the cancer cells. This technique is commonly used for prostate and skin cancers and offers a minimally invasive approach with minimal damage to surrounding tissue.
5. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC)
HIPEC is a specialized approach used in cases of abdominal cancer, such as colorectal or ovarian cancer, that has spread to the peritoneal cavity. During surgery, after removing visible tumors, heated chemotherapy is applied directly to the abdominal cavity. The heat enhances the effectiveness of the chemotherapy, and by applying it locally, higher doses can be used without systemic side effects. HIPEC is often referred to as “hot chemo” and is gaining popularity for its effectiveness in treating advanced abdominal cancers.
6. Endoscopic Surgery
Endoscopic surgery uses a flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) inserted through natural openings like the mouth or rectum to access the tumor. It’s especially useful for early-stage cancers of the digestive tract, such as esophageal or gastric cancer. Endoscopic procedures like endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) allow for precise removal of tumors without the need for external incisions.
7. Oncoplastic Surgery
For breast cancer, oncoplastic surgery combines tumor removal with reconstructive techniques to preserve or restore the breast’s appearance. This approach allows for wider tissue removal, reducing the risk of recurrence while maintaining the cosmetic outcome. It is especially beneficial for patients who wish to maintain their natural breast contour after cancer surgery.
The Benefits of Modern Surgical Techniques for Cancer Patients
 Advances in general surgery for cancer treatment have introduced significant benefits that improve outcomes, reduce complications, and enhance the quality of life for patients:
Advances in general surgery for cancer treatment have introduced significant benefits that improve outcomes, reduce complications, and enhance the quality of life for patients:
- Reduced Pain and Trauma: Minimally invasive techniques cause less damage to surrounding tissues, leading to reduced pain and faster recovery.
- Improved Precision: Robotic and laparoscopic approaches allow surgeons to operate with precision, minimizing the risk of damaging healthy tissue.
- Shorter Recovery Times: With smaller incisions and less blood loss, patients often recover faster and spend less time in the hospital.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Minimally invasive techniques are associated with a lower risk of post-operative infections, promoting better healing.
The Role of Surgery in Multidisciplinary Cancer Treatment
While surgery is often essential for cancer treatment, it is rarely the only treatment. Cancer care is highly multidisciplinary, often involving combinations of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies. A multidisciplinary team of specialists—including surgical oncologists, medical oncologists, radiologists, and pathologists—work together to create a personalized treatment plan for each patient.
For some cancers, surgery may be the first step, followed by adjuvant (post-surgical) chemotherapy or radiation therapy to target any remaining cancer cells. In other cases, neoadjuvant (pre-surgical) therapies may be used to shrink the tumor, making it easier to remove surgically. The collaboration of various specialists ensures a comprehensive approach to treatment, maximizing the chances of a successful outcome.
Recovery and Follow-Up After Cancer Surgery
Recovery from cancer surgery varies depending on the type and complexity of the procedure. Minimally invasive surgeries typically offer faster recovery times, with patients able to resume normal activities within weeks. For more extensive surgeries, such as esophagectomy or liver resection, the recovery period may be longer, and patients may require additional support in the form of physical therapy and dietary guidance.
Post-surgery, regular follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring recovery, detecting potential recurrences, and managing any side effects. Cancer patients are often placed on a follow-up plan involving periodic imaging studies, blood tests, and physical exams to ensure long-term health.
General Surgery in Cancer Treatment Conclusion: Advancing Cancer Care with Surgical Innovation
The field of general surgery continues to evolve, with new technologies and techniques improving the safety, effectiveness, and recovery times for cancer surgeries. From minimally invasive techniques and robotic-assisted surgery to innovative approaches like HIPEC and cryosurgery, patients now have more options than ever for effective, tailored cancer treatment.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with cancer and is considering surgery, consulting with a team of experienced surgeons specializing in cancer treatment can make all the difference in the journey to recovery. Contact Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery today to learn more about the latest surgical advancements and how our skilled surgeons can help in the fight against cancer.
Contact Information
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
117 E 77th Street
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
admin@lenoxmis.com
Visit our website for more information:
https://lenoxhillminimallyinvasivesurgery.com/
Esophagus Surgery: Addressing Esophageal Conditions and Surgical Treatments
 What are the major esophageal conditions and surgical treatments? The esophagus, a vital part of the digestive system, is a muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach. It plays a crucial role in the movement of food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach for digestion. However, several conditions can affect the esophagus, leading to discomfort, difficulty swallowing, and more severe health complications. In some cases, surgery may be required to treat these conditions and restore proper function.
What are the major esophageal conditions and surgical treatments? The esophagus, a vital part of the digestive system, is a muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach. It plays a crucial role in the movement of food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach for digestion. However, several conditions can affect the esophagus, leading to discomfort, difficulty swallowing, and more severe health complications. In some cases, surgery may be required to treat these conditions and restore proper function.
So let’s now explore the various esophageal conditions that may require surgical intervention, the available surgical treatments, and what patients can expect during recovery.
Common Esophageal Conditions Requiring Surgical Treatments
Several esophageal disorders may necessitate surgery, either because other treatments have failed or because the condition poses a significant health risk. Here are some of the most common conditions that could lead to surgical intervention:
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, irritating the lining. This acid reflux can cause heartburn, regurgitation, and even damage to the esophagus over time. In severe cases where lifestyle changes and medication do not provide relief, surgery may be recommended.
The most common surgical procedure for GERD is fundoplication. During this procedure, the upper part of the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophagus to strengthen the esophageal sphincter, preventing acid from flowing back into the esophagus.
2. Achalasia
Achalasia is a rare disorder in which the esophagus loses its ability to move food toward the stomach due to damage to the nerves in the esophagus. The lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscle that allows food to enter the stomach, fails to relax properly, causing difficulty swallowing and food buildup.
Surgery for achalasia typically involves a Heller myotomy, a procedure in which the surgeon cuts the muscle at the lower esophagus to help it relax and open more easily. Sometimes, this surgery is performed in conjunction with a partial fundoplication to prevent acid reflux after the procedure.
3. Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer, though less common, is a serious condition that often requires surgery as part of the treatment plan. Cancerous tumors in the esophagus can obstruct the passage of food and cause significant health complications.
The primary surgical procedure for esophageal cancer is esophagectomy, in which part or all of the esophagus is removed, and the stomach is pulled up to connect with the remaining portion of the esophagus or pharynx. In some cases, a portion of the intestine may be used to replace the removed esophagus. Esophagectomy is a complex surgery that is often accompanied by chemotherapy or radiation therapy as part of the cancer treatment plan.
4. Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus is a condition where the lining of the esophagus changes due to prolonged acid exposure from GERD. While Barrett’s esophagus itself is not cancerous, it increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer. In cases where precancerous cells (dysplasia) are present, surgery may be recommended to prevent the progression to cancer.
The surgical procedure typically performed for Barrett’s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia is endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), where abnormal cells are removed through an endoscope. In more severe cases, an esophagectomy may be required.
Surgical Treatments for Esophageal Conditions
Depending on the condition affecting the esophagus, different surgical options may be considered. Some of the most common esophageal surgeries include:
1. Laparoscopic Fundoplication
This minimally invasive procedure is often performed to treat GERD. The surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen and uses specialized instruments to wrap the upper part of the stomach around the esophagus. Laparoscopic fundoplication offers the advantages of smaller incisions, shorter recovery times, and less postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgery.
2. Heller Myotomy
Used to treat achalasia, Heller myotomy can be performed laparoscopically, allowing for a quicker recovery and reduced scarring. In this procedure, the surgeon cuts the muscle at the lower end of the esophagus to help relax it, improving the ability to swallow. A partial fundoplication may also be done during this surgery to prevent future acid reflux.
3. Esophagectomy
For esophageal cancer or other severe esophageal conditions, an esophagectomy may be necessary. During this procedure, part or all of the esophagus is removed. This surgery can be performed through the chest, abdomen, or a combination of both, and is typically followed by reconstructive surgery to restore the digestive pathway using either the stomach or intestine.
4. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
EMR is a minimally invasive procedure used to remove early-stage cancerous or precancerous tissue from the esophagus. It is performed using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera and surgical tools, which is passed down the esophagus. This procedure allows for the removal of abnormal tissue without the need for major surgery, reducing recovery time and risk.
Recovery After Esophageal Surgery
 Recovery from esophageal surgery depends on the type of procedure performed and the patient’s overall health. Minimally invasive procedures like laparoscopic fundoplication or Heller myotomy typically involve shorter hospital stays, with patients often returning home within a few days. Full recovery may take several weeks, during which patients may need to follow a special diet to aid healing.
Recovery from esophageal surgery depends on the type of procedure performed and the patient’s overall health. Minimally invasive procedures like laparoscopic fundoplication or Heller myotomy typically involve shorter hospital stays, with patients often returning home within a few days. Full recovery may take several weeks, during which patients may need to follow a special diet to aid healing.
For more complex procedures like esophagectomy, recovery may take longer. Patients may require a hospital stay of several weeks, followed by months of rehabilitation. Dietary changes, physical therapy, and follow-up care are essential to ensure proper recovery and monitor for any complications.
Choosing the Right Surgeon for Esophageal Surgery
When considering esophageal surgery, it’s crucial to choose a surgeon with specialized expertise in treating esophageal conditions. Surgeons with experience in both traditional and minimally invasive techniques can offer personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
At Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery, our team is highly skilled in treating a wide range of esophageal conditions using the latest surgical advancements. Whether you’re dealing with GERD, achalasia, esophageal cancer, or another condition, our surgeons provide comprehensive care with a focus on patient safety and optimal outcomes.
For expert consultation and surgical treatment, contact Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery:
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
117 E 77th Street
Suite 1A
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
admin@lenoxmis.com
Visit our website for more information: https://lenoxhillminimallyinvasivesurgery.com/
Digestive Disorders and General Surgery: Treatment Options and Success Stories
What are some examples of digestive disorders and general surgery that can treat them? Digestive disorders can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, leading to symptoms like pain, discomfort, and difficulty with nutrition and digestion. While many digestive conditions can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes, some require surgical intervention to resolve the underlying issue and improve overall health. Advances in general surgery have allowed for more effective and less invasive treatment options, offering patients relief from chronic symptoms and a chance at a healthier, symptom-free life.
In this article, we will explore the most common digestive disorders that require surgical intervention, the treatment options available, and some success stories that illustrate the life-changing impact of general surgery.

Common Digestive Disorders Requiring Surgery
Digestive disorders are varied in their origin and severity. Here are some of the most common conditions that may necessitate surgical treatment:
1. Gallbladder Disease
Gallbladder disease, particularly the presence of gallstones, is a common digestive issue. Gallstones can block the bile ducts, causing intense pain and inflammation, a condition known as cholecystitis. In many cases, the best course of treatment is gallbladder removal surgery, or cholecystectomy, to prevent recurrent symptoms and complications.
Success Story Example
A 45-year-old patient experienced chronic pain after meals due to gallstones. After a minimally invasive laparoscopic cholecystectomy, she was able to return to her daily activities without pain and maintain a normal diet.
2. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD occurs when stomach acid frequently backs up into the esophagus, causing discomfort and, over time, damage to the esophageal lining. For patients whose GERD is not managed with medication, surgery may be necessary. Fundoplication, where the top part of the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophagus, strengthens the valve between the esophagus and stomach, reducing reflux.
Success Story Example
A young professional in her 30s struggled with acid reflux that affected her sleep and daily functioning. After undergoing laparoscopic fundoplication, her symptoms were completely resolved, and she no longer required daily medication.
3. Hernias
A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through a weakened area in the muscle or tissue, often in the abdominal wall. In some cases, hernias can cause pain, obstruction, or other serious complications. Surgery is the definitive treatment for hernias, particularly inguinal hernias, which occur in the groin. Hernia repairs can be performed via open surgery or using minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques.
Success Story Example
A patient with a recurrent inguinal hernia that limited his ability to exercise underwent robotic-assisted hernia repair. The surgery allowed him to recover faster, and within weeks he was back to his normal workout routine, free of pain and discomfort.
4. Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) that cause inflammation in the digestive tract. In severe cases, these conditions can lead to complications such as bowel obstructions, perforations, or the development of fistulas. Surgery, such as bowel resection, may be required to remove damaged portions of the intestine and restore normal digestive function.
Success Story Example
A 28-year-old woman with severe Crohn’s disease underwent a bowel resection after multiple hospitalizations due to obstructions. Post-surgery, she reported a dramatic improvement in her quality of life and was able to achieve remission, maintaining an active lifestyle without flare-ups.

5. Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis occurs when small, bulging pouches (diverticula) in the colon become inflamed or infected. Mild cases can be managed with antibiotics, but recurring or severe cases may require surgery. Colectomy, the removal of the affected portion of the colon, is often performed to prevent future episodes of diverticulitis.
Success Story Example
After years of battling recurrent diverticulitis, a patient opted for elective surgery to remove the affected section of the colon. Following the surgery, he remained symptom-free and was able to enjoy a fiber-rich diet without fear of future flare-ups.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
One of the greatest advancements in general surgery has been the development of minimally invasive techniques. Procedures such as laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery have transformed how many digestive disorders are treated, offering patients significant benefits, including:
- Smaller incisions
- Less pain
- Reduced risk of infection
- Faster recovery times
- Minimal scarring
These techniques are particularly beneficial for surgeries involving the gastrointestinal tract, as they allow surgeons to perform complex operations with precision, while minimizing trauma to the surrounding tissues.
The Importance of Early Surgical Intervention
For many digestive disorders, early surgical intervention can prevent complications and improve outcomes. Delaying surgery in cases of severe GERD, gallbladder disease, or inflammatory bowel disease can lead to worsened symptoms, more complex surgeries, and prolonged recovery periods. Consulting with a general surgeon early in the course of the disease can provide patients with a comprehensive understanding of their condition and treatment options, including whether surgery is the best choice.
Post-Surgical Recovery and Success
The recovery process after general surgery for digestive disorders depends on the complexity of the procedure and the individual’s overall health. Minimally invasive procedures typically allow for shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times. Many patients are able to return to normal activities within a few weeks, and dietary restrictions are usually temporary.
A key component of post-surgical recovery is follow-up care, where patients may receive dietary advice, exercise recommendations, and guidance on managing any lingering symptoms. With appropriate surgical intervention and recovery support, many patients experience significant improvements in their quality of life, often returning to a normal routine free of pain and discomfort.
Digestive Disorders and General Surgery: Conclusion
Digestive disorders can have a profound impact on a person’s well-being, but with the right surgical treatment, patients can regain control of their health and experience long-lasting relief. From minimally invasive techniques for GERD and gallbladder disease to complex surgeries for conditions like Crohn’s disease and esophageal cancer, modern general surgery offers a range of effective treatment options.
If you’re considering surgery for a digestive disorder, consult with a team of highly trained general surgeons who specialize in these procedures to explore the best treatment options for your specific condition.
Contact Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery today to schedule a consultation and learn more about how their expertise can help you on the path to recovery.
Contact Information
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
117 E 77th Street
Suite 1A
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
Stomach Surgery: Surgical Procedures for Gastric Disorders
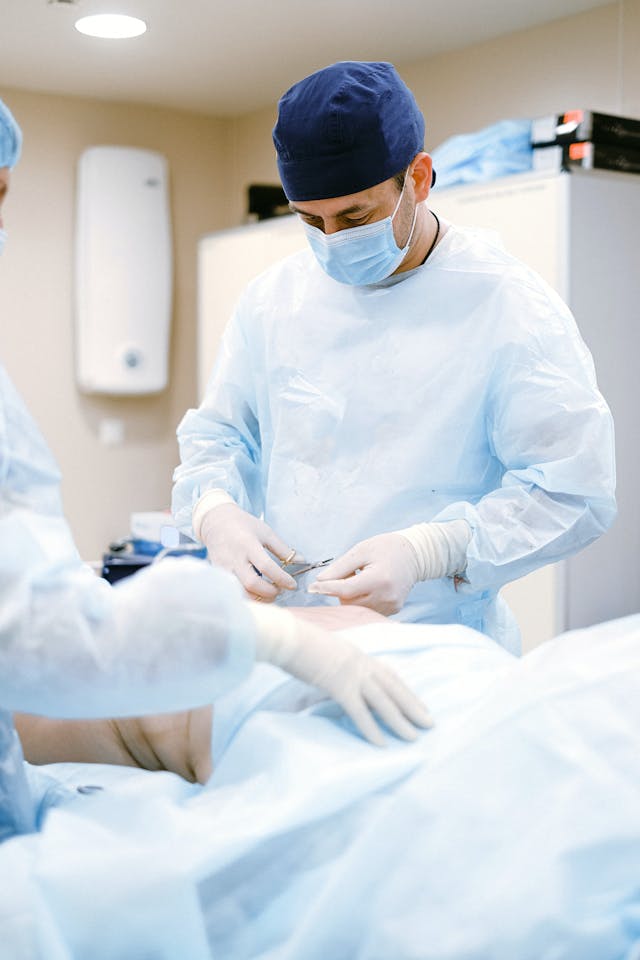 Stomach surgery is an essential treatment option for various gastric disorders, especially when non-surgical treatments such as medications and lifestyle modifications are not sufficient. Gastric disorders can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, causing discomfort, pain, and digestive issues. Fortunately, advancements in general surgery offer a range of effective surgical solutions for addressing these disorders.
Stomach surgery is an essential treatment option for various gastric disorders, especially when non-surgical treatments such as medications and lifestyle modifications are not sufficient. Gastric disorders can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, causing discomfort, pain, and digestive issues. Fortunately, advancements in general surgery offer a range of effective surgical solutions for addressing these disorders.
In this article we will explore common gastric disorders that may require surgery, the different types of stomach surgery, and what patients can expect during recovery.
Common Gastric Disorders Requiring Surgery
There are several stomach-related conditions that may require surgical intervention when conservative treatments fail. Some of the most common gastric disorders include:
1. Stomach Cancer (Gastric Cancer)
Stomach cancer occurs when malignant cells form in the lining of the stomach. Symptoms often include persistent stomach pain, nausea, unexplained weight loss, and difficulty swallowing. Early detection is crucial, and surgery is often the primary treatment option for removing cancerous tissues.
2. Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcers are open sores that develop on the inner lining of the stomach or the small intestine due to excessive stomach acid. While most ulcers can be treated with medications, severe cases that lead to bleeding, perforation, or obstruction may require surgical intervention to repair the damage and prevent further complications.
3. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is a chronic digestive disorder where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort, heartburn, and possible damage to the esophageal lining. In severe or long-standing cases of GERD, surgery may be required to prevent further complications.
4. Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis is a condition where the stomach muscles do not function properly, leading to delayed stomach emptying. This can result in nausea, vomiting, and malnutrition. Surgery may be necessary in cases where gastroparesis severely affects a patient’s quality of life and other treatments have been ineffective.
5. Obesity (Morbid Obesity)
For individuals with morbid obesity, weight loss surgery (also known as bariatric surgery) may be recommended to help achieve and maintain a healthy weight. This can also help manage or resolve related conditions like type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
Types of Stomach Surgery
There are several surgical options for treating stomach-related disorders. The choice of surgery depends on the specific condition, the severity of the disease, and the overall health of the patient. Some of the most common types of stomach surgery include:
1. Gastrectomy
A gastrectomy involves the partial or complete removal of the stomach and is most commonly used to treat stomach cancer. There are three main types of gastrectomy:
- Partial Gastrectomy: In this procedure, only the cancerous part of the stomach is removed, and the remaining portion is reconnected to the small intestine.
- Total Gastrectomy: The entire stomach is removed, and the esophagus is connected directly to the small intestine.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: This procedure, often used in bariatric surgery, involves removing a large portion of the stomach, leaving behind a tube-like structure that limits food intake.
2. Fundoplication
Fundoplication is a surgical procedure often used to treat severe GERD. During the procedure, the top of the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophagus to strengthen the esophageal sphincter and prevent acid reflux. This surgery can be performed laparoscopically, offering the benefits of smaller incisions, less pain, and a faster recovery.
3. Bariatric Surgery (Weight Loss Surgery)
Bariatric surgery is performed to help patients with morbid obesity achieve significant weight loss and manage obesity-related health conditions. The most common types of bariatric surgery include:
- Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y): In this procedure, a small stomach pouch is created, and a portion of the small intestine is rerouted to bypass the majority of the stomach and the first section of the small intestine. This limits food intake and calorie absorption.
– Sleeve Gastrectomy: As mentioned earlier, this procedure involves removing a large portion of the stomach, creating a smaller stomach “sleeve” that restricts food intake. - Adjustable Gastric Banding: A silicone band is placed around the upper portion of the stomach to create a small stomach pouch, limiting how much food can be eaten at one time.
4. Pyloroplasty
Pyloroplasty is a procedure used to treat conditions like gastroparesis by widening the pylorus, the passage between the stomach and the small intestine. This allows for easier passage of food from the stomach to the intestines, improving digestion and reducing symptoms like nausea and vomiting.
5. Vagotomy
A vagotomy is a surgical procedure where the vagus nerve, which stimulates acid production in the stomach, is cut to reduce acid secretion. This surgery is sometimes performed in conjunction with a gastrectomy to treat peptic ulcers that are resistant to other treatments.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
Many of the procedures mentioned above can be performed using minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy or robotic-assisted surgery. These techniques offer several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
- Smaller incisions and less scarring
- Reduced post-operative pain
- Shorter hospital stays
- Faster recovery times
- Lower risk of infection
For patients who qualify, minimally invasive surgery can provide excellent outcomes with fewer complications and a quicker return to daily activities.
Recovery After Stomach Surgery
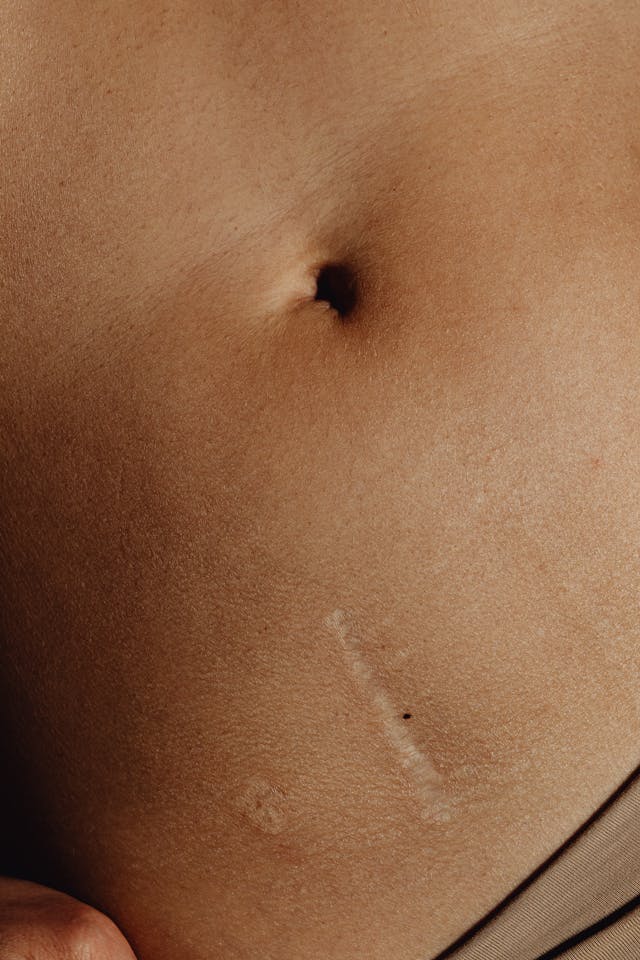
Recovery from stomach surgery varies depending on the specific procedure and the patient’s overall health. In general, patients who undergo minimally invasive procedures tend to recover more quickly than those who have traditional open surgery. Here are some general guidelines for what to expect during recovery:
- Hospital Stay: Most patients will need to stay in the hospital for a few days after surgery. During this time, they will be monitored for complications and receive pain management and nutrition through an IV.
- Dietary Changes: After stomach surgery, patients will need to follow a specific diet, often starting with liquids and gradually transitioning to solid foods. A nutritionist will work with patients to create a diet plan that supports healing and meets nutritional needs.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients will be encouraged to move around soon after surgery to prevent blood clots, but strenuous activities and heavy lifting will need to be avoided for several weeks.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor healing, address any complications, and ensure that the stomach is functioning properly.
Stomach Surgery & Surgical Procedures for Gastric Disorders: Conclusion
Stomach surgery can be a life-changing intervention for those suffering from chronic gastric disorders. Whether it’s addressing cancer, severe acid reflux, peptic ulcers, or obesity, surgical treatments can provide lasting relief and improve quality of life. With the availability of minimally invasive techniques, patients can now experience faster recovery times and fewer complications.
If you’re experiencing persistent gastric issues or have been diagnosed with a condition that may require surgery, it’s essential to consult with an experienced surgeon who specializes in stomach surgery.
For more information or to schedule a consultation, contact the expert surgeons at Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery. They provide personalized treatment plans using the latest surgical advancements to help patients achieve the best possible outcomes.
Contact Information
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
117 E 77th Street
Suite 1A
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
admin@lenoxmis.com
Minimally Invasive Surgery: Benefits and Procedures
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has revolutionized the field of surgery, offering numerous benefits over traditional open surgery. This guide explores the advantages and common procedures associated with minimally invasive techniques.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery involves smaller incisions compared to traditional surgery, which leads to several key benefits:
- Reduced Pain: Smaller incisions result in less tissue damage, leading to decreased postoperative pain and discomfort.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Patients typically experience faster recovery times, allowing them to return to normal activities sooner.
- Lower Risk of Infection: The smaller incisions used in MIS reduce the risk of infection and other complications.
- Minimal Scarring: With less tissue disruption, patients benefit from minimal scarring and improved cosmetic outcomes.
- Reduced Blood Loss: MIS techniques often involve less blood loss during surgery, reducing the need for blood transfusions.
Common Minimally Invasive Procedures
Several surgical procedures can be performed using minimally invasive techniques. Here are some of the most common ones:
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light at the end (a laparoscope) to view the inside of the abdomen. Surgeons make small incisions to insert surgical instruments and perform procedures such as gallbladder removal, hernia repair, and appendectomy.
Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is used to diagnose and treat joint problems. A small camera, called an arthroscope, is inserted into the joint through a tiny incision. This technique is commonly used for procedures on the knee, shoulder, elbow, and wrist.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery involves the use of robotic systems to enhance the precision and control of the surgeon. The surgeon operates the robot from a console, allowing for highly accurate movements. This technique is often used for complex procedures such as prostate surgery, hysterectomy, and cardiac surgery.
Endoscopic Surgery
Endoscopic surgery involves using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera, to access internal organs and tissues. This technique is commonly used for gastrointestinal procedures, such as removing polyps from the colon or treating conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Patient Eligibility for Minimally Invasive Surgery
Not all patients are candidates for minimally invasive surgery. Factors such as the type and severity of the condition, patient health, and previous surgical history play a role in determining eligibility. A thorough evaluation by a qualified surgeon is essential to decide the best surgical approach.
Preparing for Minimally Invasive Surgery
Preparation for MIS involves several steps, including preoperative evaluations, discussing medication adjustments, and understanding the procedure and recovery expectations. Patients should follow all preoperative instructions provided by their surgeon to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Postoperative care following MIS is typically less intensive than traditional surgery. Patients can expect shorter hospital stays, quicker return to normal activities, and less postoperative pain. However, it is crucial to follow the surgeon’s postoperative instructions to promote optimal healing and prevent complications.
Minimally Invasive Surgery: Conclusion
Minimally invasive surgery offers numerous benefits, including reduced pain, shorter recovery times, lower risk of infection, minimal scarring, and reduced blood loss. Understanding the procedures and preparing adequately can help ensure a successful outcome.
For expert guidance on minimally invasive surgery and to determine if you are a candidate, contact Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery.
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
117 E 77th Street
Suite 1A
New York, NY 10075
Phone: 646-846-1136
Email: admin@lenoxmis.com
Post-Surgery Recovery Tips: How to Heal Faster
Post-surgery recovery is a critical phase that requires careful attention and adherence to medical advice. Here are some essential tips to help you heal faster and more effectively.
Follow Postoperative Instructions
Adhering to your surgeon’s postoperative instructions is crucial for a smooth recovery. These guidelines are tailored to your specific surgery and include advice on wound care, medication, activity levels, and follow-up appointments.
Manage Pain Effectively
Pain management is essential for recovery. Take prescribed pain medications as directed and use additional methods like ice packs, elevation, and rest to alleviate discomfort. Discuss any pain management concerns with your healthcare provider.
Maintain a Healthy Diet
Nutrition plays a vital role in healing. Eat a balanced diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals to support tissue repair and boost your immune system. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
Stay Active, but Rest Appropriately
Light physical activity, such as short walks, can promote blood circulation and prevent complications like blood clots. However, avoid strenuous activities that might strain your surgical site. Follow your surgeon’s advice on when and how to resume normal activities.
Monitor for Signs of Complications
Watch for signs of complications, such as increased pain, swelling, redness, fever, or discharge from the surgical site. Early detection and prompt communication with your healthcare provider can prevent minor issues from becoming serious.
Attend Follow-Up Appointments
Follow-up appointments allow your surgeon to monitor your progress and address any concerns. Attend all scheduled visits and discuss any symptoms or issues you’re experiencing.
Practice Good Wound Care
Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and promote healing. Keep the surgical site clean and dry, and follow your surgeon’s instructions for changing dressings. Avoid soaking the wound in water until it is fully healed.
Get Plenty of Rest
Rest is vital for recovery. Ensure you get adequate sleep and take naps as needed. Resting helps your body repair tissues and regain strength.
Avoid Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking and alcohol can impair the healing process. Avoid these substances during your recovery period to ensure optimal healing.
Stay Positive and Patient
Recovery takes time, and maintaining a positive attitude can help you stay motivated and adhere to your recovery plan. Be patient with yourself and allow your body the time it needs to heal fully.
Post-Surgery Recovery: Conclusion
By following these post-surgery recovery tips, you can enhance your healing process and reduce the risk of complications. Always communicate with your healthcare provider about your progress and any concerns you may have.
For personalized post-surgery care and support, contact the specialists at Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery. Our highly experienced surgical team is dedicated to providing the highest quality care throughout your recovery journey.
Contact Information:
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
117 E 77th Street
Suite 1A
New York, NY 10075
646-846-1136
admin@lenoxmis.com
https://lenoxhillminimallyinvasivesurgery.com/
Preparing for Surgery: A Patient’s Guide
Preparing for surgery can be a daunting experience, but proper preparation can help ensure a smoother process and recovery. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you get ready for your surgical procedure. Preparing for Surgery Preoperative Instructions Follow all preoperative instructions provided by your surgeon. These may include dietary restrictions, medication adjustments, and fasting requirements.… Continue Reading
Top 10 Signs You Might Need Surgery
What are the top 10 signs you might need surgery? Recognizing the signs that you might need surgery is crucial for timely intervention and effective treatment. Here are the top things to watch for. Top 10 Signs You Might Need Surgery 1. Chronic Pain Persistent, severe pain that doesn’t improve with medication or other treatments… Continue Reading
Understanding the Role of a General Surgeon: What You Need to Know
Understanding the role of a general surgeon is crucial for anyone facing surgery or seeking to understand the broad field of general surgery. General surgeons are highly trained medical professionals who perform a variety of surgical procedures, often involving critical and life-saving operations. What Does a General Surgeon Do? General surgeons are skilled in a… Continue Reading
Liver Surgery: Procedures for Liver Diseases and Tumors
In this article, we will explore common liver conditions, their symptoms, and the surgical procedures for liver diseases and tumors. The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous functions, including detoxification, metabolism, and the production of essential proteins. However, various conditions can affect the liver, ranging from benign liver cysts to liver tumors. When… Continue Reading
Robotic Assisted General Surgery: Advancements in Manhattan
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the benefits of robotic assisted general surgery and how it is transforming the landscape of surgical procedures. Advancements in surgical technology have revolutionized the field of general surgery, providing surgeons with innovative tools and techniques to deliver improved outcomes for patients. One such advancement is robotic-assisted surgery, which… Continue Reading
Adrenal Gland Disorders: Surgical Approaches and Treatment Considerations
In this informative article, we will explore common adrenal gland disorders, their symptoms, and the surgical treatment options available. The adrenal glands, located on top of each kidney, are responsible for producing essential hormones that regulate various bodily functions. However, certain conditions can disrupt the normal functioning of the adrenal glands, leading to adrenal gland… Continue Reading
Preparing for General Surgery: A Step-by-Step Guide
In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through the key aspects of preparing for general surgery to help you feel confident and informed. Facing the prospect of general surgery can be daunting, but proper preparation can help alleviate anxiety and ensure a smoother recovery process. Whether you’re scheduled for a routine procedure or a… Continue Reading
Gallbladder Surgery: Common Disorders and Surgical Solutions
Various conditions can affect the gallbladder, leading to discomfort and potential complications. Gallbladder surgery may be necessary when conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms. The gallbladder is a small organ located beneath the liver that plays a vital role in the digestion of fats. At Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery, a leading general surgery practice… Continue Reading
Common General Surgeries and Their Importance for Patients
When it comes to addressing various health conditions and improving quality of life, general surgery plays a crucial role. General surgeons are skilled professionals who specialize in a wide range of surgical procedures. At Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery, a renowned general surgery practice in New York City, our team of expert surgeons is dedicated… Continue Reading
Understanding Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally Invasive Procedures in Manhattan
In this informative article, we will explore laparoscopic surgery, its advantages, and the range of procedures it encompasses. Advancements in surgical techniques have revolutionized the field of medicine, allowing for more precise and minimally invasive procedures. Laparoscopic surgery, also known as keyhole surgery, has gained popularity for its numerous benefits compared to traditional open surgery.… Continue Reading
Appendix Surgery: Understanding Appendicitis and Surgical Interventions
In this informative article, we will explore appendicitis, its symptoms, and the surgical interventions available for its treatment. The appendix may be a small organ in the human body, but when it becomes inflamed, it can cause significant pain and discomfort. Appendicitis is a common condition that often requires surgical intervention to prevent complications. At… Continue Reading